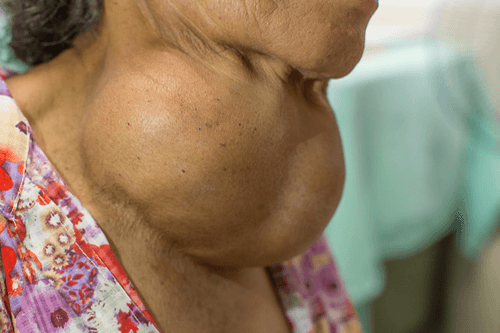
Thyromegaly – A big thyroid gland called a goiter, can happen for different reasons. Common causes include insufficient iodine and making too much or too little of certain thyroid hormones called T3 and T4. Other illnesses like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s disease can also make your thyroid gland bigger. Let’s know more about Thyromegaly, its causes and prevention. Stay tuned with us until the end of the article:
Can a big thyroid gland make it hard to swallow?
Usually, a goiter or a big thyroid gland doesn’t hurt. But if it’s really big, it might make it tough to breathe or swallow. It can also make you cough and feel like your throat is tight.
Can you make a big thyroid gland smaller?
If your thyroid is too big, doctors can make it smaller with medicine. They often give you a synthetic thyroid hormone called L-thyroxine. Sometimes, they use radioactive iodine to shrink the thyroid without hurting other parts. In severe cases, you might need surgery when the goitre presses on nearby tissues.
Basic Information about Thyroid Enlargement
The thyroid is an important part of our body. It makes hormones that control how we use energy, our body temperature, and how we grow.
When the thyroid doesn’t work right, it can cause problems. Studies show that about 200 million people around the world have thyroid issues.
A big problem with the thyroid gland is Thyromegaly, where it gets too big. This can cause many health issues, and sometimes it can even mean cancer.
There have been about 62,450 new cases of Thyroid Cancer lately. It’s important that people learn about thyroid problems and how to stop them from happening.
What is thyromegaly?
Thyromegaly is when your thyroid gland gets too big and can be seen as a bulge in your neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It happens when your thyroid gland doesn’t work right.
Most of the time, women are more likely to get thyromegaly than men of the same age. Sometimes, it’s because of family history.
What are the main reasons for thyromegaly?
Thyromegaly can happen because of different things like your body’s defense system going wrong and attacking your thyroid, which can lead to problems like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
In some cancer cases, doctors might need to take out part or all of the thyroid gland to stop the cancer from spreading. But then, the thyroid can’t make enough hormones for your body.
Radiotherapy: Sometimes, people with diseases like Grave’s disease, thyroid cancer, or nodular goitre get treated with radioactive iodine (I-131). Also, those with cancers in their head and neck area, Hodgkin’s disease, or lymphoma may get radiation therapy. But these treatments can make the thyroid gland bigger.
Birth Defect: Some babies are born with thyroid glands that are not normal. They might have a thyroid that’s not fully formed or in the wrong place (called ectopic thyroid). In other cases, the thyroid doesn’t work like it should. All of these things can make the thyroid swell up.
Thyroiditis happens when the thyroid gland gets inflamed because of autoimmune diseases or viral infections. It can make many thyroid hormones go into the blood at once, causing a short time of too much thyroid hormone followed by too little.
Medications: Some over-the-counter drugs like interleukin-2, amiodarone, lithium, and interferon alpha can mess up how your thyroid makes hormones. If your family has a history of hypothyroidism or autoimmune diseases, you might be more likely to have this happen.
Iodine Imbalance: If you don’t have enough iodine in your body or your daily diet, your thyroid gland can get bigger.
Pituitary Gland Problems: The pituitary gland controls how the thyroid gland makes hormones. Radiation therapy, cancerous tumours, or surgeries can damage the pituitary gland and lead to a bigger thyroid gland.
Existing Illness: Some diseases you might already have, like amyloidosis (when proteins build up), sarcoidosis (a condition with granulomas), or hemochromatosis (when iron builds up), can mess up how your thyroid works and make it bigger.
Family History: If your family has a history of hypothyroidism or other hormone problems, you might have a higher chance of getting a swollen thyroid.
Don’t want to keep searching for natural fixes for your thyroid problems? Give these safe and proven solutions a try to make your thyroid better.
What are the symptoms of thyromegaly?
Thyromegaly, also known as goitre, is a thyroid gland enlargement. The thyroid gland is butterfly-shaped in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
The symptoms of thyromegaly can vary depending on the size and location of the enlarged thyroid gland. Some people may not have any symptoms, while others may experience:
- A lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness
- Coughing
- Pain in the neck
- Pressure on the throat
- Changes in the voice
- Fatigue
- Weight gain or loss
- Heat intolerance
- Cold intolerance
- Anxiety
- Depression
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment.
What are the different kinds of thyroid enlargement
- Aberrant type: When there’s extra thyroid tissue swelling.
- Adenomatous type: Caused by growths or many lumps in the thyroid.
- Basedow type: This happens when the thyroid works too much after getting iodine.
- Colloid type: The thyroid gets big and soft with a jelly-like substance.
- Cystic type: Cysts form because of mucus or jelly-like stuff.
- Endemic type: Only happens in certain areas.
- Fibrous type: The covering around the thyroid and its support tissue grows too much.
- Follicular type: The main part of the thyroid is affected.
- Intrathoracic type: Part of the thyroid pushes into the chest.
- Iodide type: Caused by too much iodine.
- Multinodular type: Bumps form inside the thyroid.
- Parenchymatous type: The thyroid’s tiny parts grow more.
- Perivascular type: Around a big blood vessel.
- Retrovascular type: Behind a big blood vessel.
- Substernal type: The bottom part goes below the breastbone.
- Vascular type: Blood vessels in the thyroid get bigger.
Treatment and Stopping It from Happening
The treatment for thyromegaly depends on how bad it is. If it’s not too bad, the doctor might watch and see. They might also tell you to change what you eat.
The doctor might give you potassium iodide if you don’t have enough iodine. They can also give you medicine to control the swelling of your thyroid.
But if it’s really bad or you have thyroid cancer, surgery is the best way to fix it.
FAQs
What is thyromegaly?
Thyromegaly is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes enlarged. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It produces hormones that help regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
What are the causes of thyromegaly?
The most common cause of thyromegaly is iodine deficiency. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. Other causes of thyromegaly include:
- Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s disease and Graves’ disease
- Thyroid nodules
- Thyroid cancer
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland)
- Medications such as lithium and amiodarone
What are the symptoms of thyromegaly?
The symptoms of thyromegaly vary depending on the size of the enlarged thyroid gland. Some people may not have any symptoms, while others may experience:
- A lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Weight gain or loss
- Sensitivity to heat or cold
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
How is thyromegaly diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose thyromegaly by looking your neck and ordering blood tests to measure your thyroid hormone levels. You may also need other tests, such as an ultrasound or a biopsy.