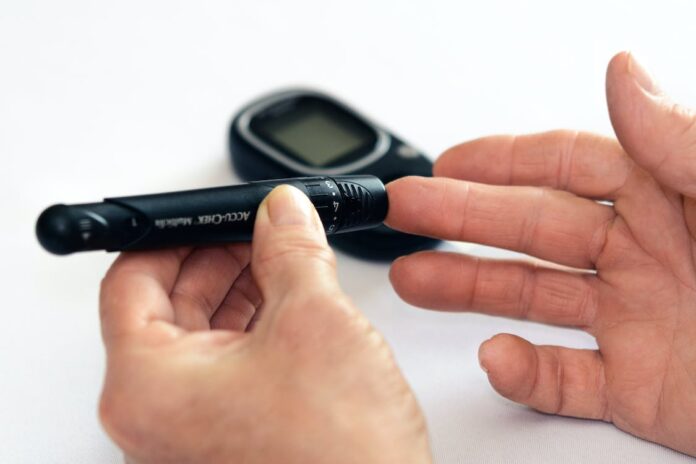
What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus, also known as just diabetes, is a metabolism condition that raises blood glucose levels. Insulin is the hormone that transports sugar from the blood to the cells, where it can be retained or utilized as fuel. When you have diabetes, the body can’t use the insulin this does produce, or it doesn’t produce enough of it.
Diabetes-related high blood sugar levels left untreated can harm your kidneys, nerves, eyesight, and other organs. However, one can safeguard your health by learning about diabetics and implementing steps to avoid or control it.
Varieties of diabetes
There are wide varieties of diabetes:
- Type1: Diabetes type 1 is just an autoimmune condition. The immune response targets and kills insulin-producing cells within the pancreas. Uncertainty surrounds the attack’s origin.
- Type2: If your body gets intolerant to insulin, type 2 diabetes develops, and levels of blood sugar rise. Around 90% – 95% of individuals who are diabetic have type 2, making it the most prevalent kind.
- Diabetes gestational: Diabetes gestational is excessive blood glucose when pregnant. This form of diabetes is brought on by substances the placenta secretes that inhibit insulin.
- Despite having an identical name to diabetes mellitus, the uncommon illness known as insipidus is unrelated. Your kidneys are removed from your body with excessively liquid in a separate ailment. Different diabetes types have different signs, diabetes symptoms, and treatment options.
Prediabetes
The title “prediabetes” is used when your blood glucose is greater than normal but not severe enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. It happens if your body’s cells do not react to insulin as they ought to. Later on, type 2 diabetes may result from all this.
According to specialists, more than one-third of Americans have prediabetes, but more than an 80percent of those individuals are completely unaware of their condition.
The signs of diabetes
Blood glucose increases accompany the onset of diabetes.
Common Symptoms
Typical diabetes symptoms and signs involve:
- Increased appetite
- Heightened thirst
- Slim down
- Excessive urination
- Hazy vision
- Extreme exhaustion
- Not-healing wounds
The symptoms in males
Men experiencing diabetes can exhibit the following symptoms along with the usual ones:
- A diminished lust for life
- Erection problems (ED)
- Weak muscle power
Signs in women
Diabetes in women may cause symptoms like:
- Vulvar aridity
- Diseases of the urinary system
- Candida infections
- Itching, dry skin
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes signs could include:
- Severe hunger
- Heightened thirst
- Unintended loss of weight
- Excessive urination
- Hazy vision
- Drowsiness
- It might also cause alterations in mood.
Diabetes Type 2
Type 2 diabetes signs can also include:
- Increased appetite
- Heightened thirst
- More frequent urine
- Hazy vision
- Drowsiness
- Taking a long time to heal sores
- Moreover, it might lead to recurrent infections. This occurs because the body has a tougher time healing when glucose levels are elevated.
Gestational diabetes
The majority of women who acquire gestational diabetes have no diabetes symptoms. Medical practitioners frequently find the issue when doing a regular dental glucose endurance test or sugar levels test, typically done between the 24th – 28th week of pregnancy. A person having gestational diabetes may, in extremely rare circumstances, also feel an increased desire for urine.
Causes of Diabetes
Each form of diabetes has a distinct set of reasons.
Diabetes Type 1
Type 1 diabetes has an unknown specific cause, according to doctors. The pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin are wrongly attacked and destroyed by the body’s immune system. Certain people may indeed be affected by their genetics. Additionally, a virus may trigger an immune response assault.
Diabetes Type 2
The common causes of diabetes are a result of both hereditary and environmental factors. Your risk is further increased if you are overweight or obese. The impacts of insulin on blood glucose are resisted by your organs when you are overweight, particularly in the abdomen. Families are prone to this condition. The family members have genetics that increases their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Gestational diabetes
Hormonal shifts during pregnancy are the cause of gestational diabetes. The placenta secretes hormones that reduce the overall sensitivity of a pregnant person’s cells to the consequences of insulin. Pregnancy-related elevated glucose levels can result from this.
Risk elements for diabetes
Your risk of diabetes is influenced by several things.
Diabetes Type 1
Type 1 disease is higher among children and teenagers, people with a genetic link with the illness, and people with specific genes connected to such a condition.
Diabetes Type 2
You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you:
- A weight issue
- And older than 45 years
- Possess a parent or sibling who is afflicted
- Are not active physically
Gestational Diabetes
You run a higher chance of developing gestational diabetes if you:
- A weight issue
- Are you older than 25
- Formerly pregnant and have gestational diabetes
Complications related to Diabetes
Your parts of the body are damaged by impaired glucose tolerance. The possibility of consequences increases as your blood sugar level rises and you survive with it after a prolonged period.
Consequences associated with type 2 diabetes encompass:
- Heart illness, cardiac arrest, and stroke.
- Neuropathic
- Nephropathy
- Retinal detachments and reduced vision
- Hearing impairment
Diet and Diabetes
Many questions arise: What is the best breakfast for a diabetic to eat? An essential component of diabetes management is good nutrition. In certain circumstances, altering your diet may be sufficient to control the condition.
Diabetes type 1
The varieties of meals you eat determine whether your blood glucose levels rise or lower. Food products that are rich in starch or full of sugar cause a sharp rise in blood glucose levels. Gains in fat and protein happen less gradually. Your team doctor might advise you to restrict the number of carbohydrates you consume each and every day. Additionally, you must regulate your insulin dosages with your calorie consumption.
Diabetes Type 2
The proper meal choices can control your blood glucose levels and reduce body fat. A crucial component of dieting for Type 2 diabetes is carbohydrate monitoring. You can calculate how many grams of carbohydrates to consume at every meal with the aid of a dietician. Try to spread your lunches and dinners during the day to help maintain stable blood glucose levels. Give priority to nutritious foods like:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Whole grains
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, you must have understood ‘What is diabetes?’ some forms of diabetes, such as type 1, are brought on by external sources and are common causes of diabetes. Others, like type 2, can be avoided by improving dietary habits, what is the best breakfast for a diabetic to eat, upping physical activity, and decreasing weight. With your doctor, go over the dangers of diabetes. Have your blood sugar checked if you’re at risk, and then manage your blood sugar according to your doctor’s recommendations.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q1) What ought my blood sugar to be?
Ans: The American Diabetes Association suggests a blood glucose variety between eighty (80) – a hundred thirty (130) earlier than food and much less than one hundred eighty approximately 2 hours after a meal. This variety ought to go to the vicinity of your A1c below 7.
Q2) What can I consume if I even have diabetes?
Ans: One can consume pretty much whatever they want. It is set to understand the right component sizes and what sort you’re placing for your plate. A nutritionist allows you to discover ways to matter carbs, with meal-making plans and what is the best breakfast for a diabetic to eat.