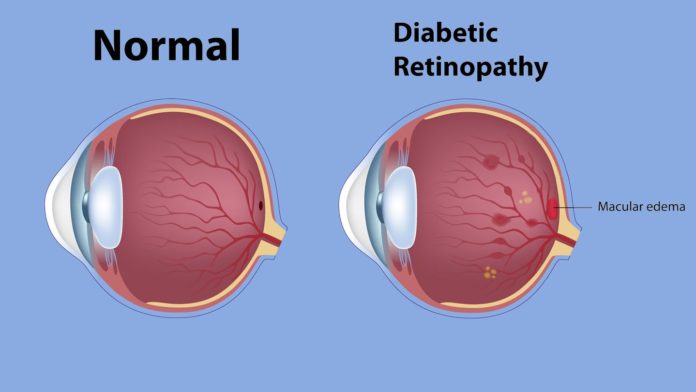
Diabetics are prone to developing many types of damage in their bodies because of high blood sugar levels. One of the areas most prone to damage development is the eyes. Diabetics can suffer from a condition called diabetic macular edema. This type of eye condition causes a buildup of fluid around the macula of the eye, which can result in vision disturbances.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Macular Edema?
Those who have diabetes need to be aware of the dme symptoms so they can take action to seek medical care right away. The following are some of the most common symptoms that present with diabetic macular edema. If a person notices any of these symptoms, they should see an eye doctor right away for an examination and diagnosis.
- Blurred vision is one of the first symptoms people notice when they have DME.
- When individuals look at certain colors, they may appear faded.
- Some people develop double vision with diabetic macular edema.
- Increased floaters in the eyes is also a sign of DME.
What Are the Causes of Diabetic Macular Edema?
When someone has diabetes, their consistent high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the small blood vessels that are in the eye. When blood vessel damage occurs, the risk of developing diabetic macular edema greatly increases.
To keep the eyes protected, individuals must work with their medical team to ensure their blood sugar levels stay as close as normal as possible. High blood pressure and high cholesterol may also cause blood vessel damage in the eyes. When diabetes is combined with these conditions, the risk of developing DME increases exponentially.
Kinds of Diabetic Macular Edema
Multiple kinds of DME exist. The type of DME is based on the severity of the edema in the macula. When the retina is thick, this means great swelling is occurring. Thicker retinas also signify a greater level of vision disturbance. The damage may be done widespread or simply occur in one isolated area of the eye. An eye doctor will determine the severity of the condition based on the findings from the following types of tests.
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) is a test that measures the level of swelling in the retina of the eye.
- Fluorescein Angiography is a dye test that highlights blood flow to the eye area.
- Fundus Imaging takes highly detailed pictures of the retina so the doctor can look for any irregularities in the blood vessels of the eye.
How Is Diabetic Macular Edema Treated?
Treating DME as soon as possible is essential. The goal of treatment is to relieve the pressure and swelling of the retina so vision disturbances are reduced. In some cases, more than one treatment may be recommended by an eye doctor. The following are some of the top treatments for DME.
- Laser therapy can be used to seal leaking blood vessels and help reduce the swelling in the macular area.
- Injectable medications are used to treat the blood vessels of the eye and prevent them from abnormally growing and causing swelling.
- Steroids may also be used and often are delivered in conjunction with one of the above DME treatments.
Prevention Is Essential
Protecting the eyes against DME is essential for diabetics. The main form of prevention is found in keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible. When blood sugar rises high often, blood vessel damage results. Diabetics need to make sure they are seeing the eye doctor for their annual eye examinations to find the signs of DME early.