Plants Hormone – Hormones act like chemical messengers made in one part of the body and deliver signals to different body parts. We know hormones play an important role in the human body but did you know even plants have hormones too?
Plants do not experience a change in voice, body hair, and acne; however, hormones have an amazing effect on plants. Keep reading to find out how.
Types Of Plant Hormones and Their Functions
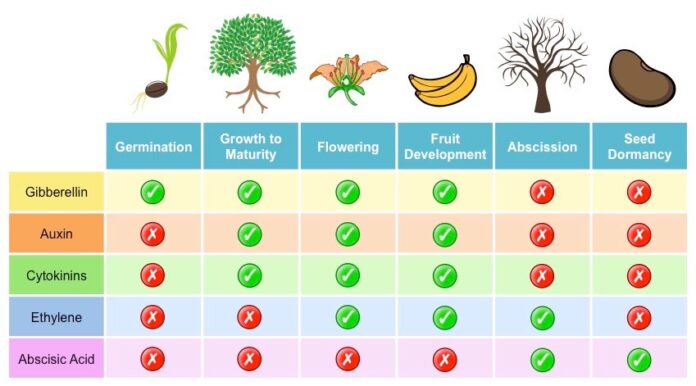
This article will cover five main types of plants hormone – auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, and abscisic acid. All these hormones work together for plant growth.
What are Plant Hormones and their functions?
Plants need water, sunlight, minerals, and oxygen for development and growth. All these are external factors; however, plants also need internal factors that help regulate growth and development. These internal factors are phytohormones or plant hormones.
Plant hormones are in low concentrations and derivatives of gases, adenine, terpenes, and indole. Sometimes hormones act synergically, and sometimes individually. These play a major role in processes like phototropism, vernalization, dormancy, seed germination, etc.
Auxin Hormone
Auxin refers to “grow.” These are commonly used in horticultural and agricultural practices. Auxin hormones are also found in the roots and stems of apices and later migrate to other parts of the plant.
Functions:
- Elongation of roots and stems
- Apical dominance: Suppressing the growth of lateral buds
- Induces parthenocarpy: growth of fruits and veggies without the help of fertilization
- Preventing premature falling of flowers, leaves, and fruits
- Helps in cutting the stem and grafting to start rooting
- Inducing flowering, like in pineapple
- Helps in dividing cells and xylem
Gibberellins Hormone
In plants, there are 100 plus Gibberellin hormones. These hormones are acidic and are commonly found in fungi and higher plants.
Functions:
- These hormones help in bolting- elongation of internodes before flowering in beet and cabbage.
- Delaying senescence
- Promoting parthenocarpy
- Reversing dwarfism and elongating stem
- Inducing maleness in cannabis
- Forming hydrolytic enzymes, germinating cereal grails, barley seeds
- Breaking seed dormancy
Cytokinins Hormone
Cytokinin plants hormone play a key role in the cytokinesis process. These are naturally synthesized in plant areas where cell division occurs, like shoot buds, root apices, and baby fruits. Cytokinins move in polar and basipetal movements.
Functions:
- Cytokinins help in promoting adventitious and lateral shoot growth
- Overcoming apical dominance caused by auxins
- Inducing chloroplast formation in leaves
- Promoting nutrient mobilization and delaying leaf senescence
Abscisic Acid Function
Abscisic is a growth-inducing hormone. These act as antagonists to the GAs. Abscisic stops plant metabolism and also regulates dormancy and abscission. It is also known as a stress hormone because it increases the tolerance level of plants.
Functions:
- Promotes leaves and fruits abscission
- Prevents seed germination
- Promotes leaves senescence
- Boost seed dormancy for storage purposes
- Stimulates stomata closure to prevent the transpiration process under water stress.
Ethylene Plant Hormone
Ethylene plant hormones work as a growth inducer and inhibitor. These are present in gaseous form and are synthesized in ripe fruits. It also helps regulate the physiological process and is widely used in agriculture.
Functions:
- Boosts fruit ripening process
- Controls leave epinasty
- Breaks bud and seed dormancy
- Stimulates elongation of internodes and petioles
- Promotes abscission and senescence of flowers and leaves
- Boosts root hair and root growth, thereby enhancing absorption
- Stimulates femaleness in monoecious plants.
- Formation of apical hook in dicot seedlings
These are the five main types of plant hormones and their functions. However, other plants hormone also affect a plant’s physiological process, like salicylates, brassinosteroids, strigolactones, jasmonates, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the two major types of phytohormones?
The two main types of phytohormones are growth inhibitors and growth promoters.
Name a few phytohormones.
There are five phytohormones – gibberellins, auxins, ethylene, cytokinins, and abscisic acid.
What is the key role of cytokinins?
It helps promote adventitious and lateral shoot growth, which helps initiate shoot growth and overcome auxins-induced apical dominance.
Read More: Types Of Plant Hormones and Their Functions