Types Of Cells – Cells are tiny structures present in the human body. These small cells are trillions in our body, and these cells come together to make organs; these organs form the organ system, and that system runs the human body. To form an organ, they come to form a tissue, and that tissue further develops into an organ. Cells are tiny structures without which no living organism can exist.
Every cell present in our body has different responsibilities and functions. For instance, the cells of our digestive systems have different functions than that present under our first layer of skin or in our skeletal system. They may have different roles in our bodies but rely on each other to function properly. Now, there are over a thousand types of cells present today. Here are the eleven most common cells we found:
Types Of Cells In Our Body
Let’s take a look at the basic 11 types of cells in a human body.
Stem Cells
Stem cells in our body have the role of repairing damaged tissues. They are unique in their way, as they are initially unspecialized cells, and they develop their way up to specialized cells. To repair the damage, they divide and replicate themselves to repair and replenish. Scientists are often seen taking advantage of the stem cells’ property of regenerating themselves for tissue repair, organ transplant, and several treatments of disease.

Blood Cells
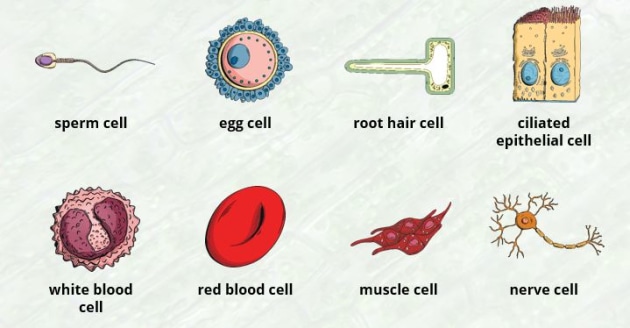
One of the most vital cells is present in our body. The bone marrow forms blood cells to transport oxygen throughout the body and fight infections in certain areas. Blood cells have a very important responsibility in our body.
Blood cells are made from three types of blood cells; these three subcategories also carry different responsibilities. The three types are Red Blood cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets.
Red Blood cells are used for the transportation of oxygen throughout the body and also make up for the type of blood you carry.
Whereas the White Blood cells are the defense mechanism of our body. They fight pathogens and other viruses and provide immunity to our bodies.
Platelets help prevent excessive blood loss due to damaged blood vessels by helping the clotted blood.
Muscle Cells
For our body to move and work, muscle cells come together to form muscle tissue to help our body have movement. And just like blood cells, muscle cells are sub-categorized into three cells. Namely, skeletal muscle cells, cardiac muscle cells, and smooth muscle cells.
A skeletal Muscle cell is attached to the bone and is responsible for our muscles’ voluntary movement. Not only movement but this tissue also protects and supports bundles of muscle fibers.
Then comes the cardiac muscle cells, responsible for involuntary movement in our body. They are present in the heart and help it function through constant synchronized movement. They are interconnected together through intercalated discs.
Smooth Muscle is also the involuntary muscle that helps cover and line important organs of our body, like kidneys, liver, lungs, and intestines. Other than the lining, they also fill the cavities.
Bone Cells
Bone cells are the major part of our skeletal systems and mineralized tissue. Bones are usually made of calcium phosphate and a blend of collagen. Now again, three types of bone cells are present in our body. Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts, and osteocytes.
Osteoclasts are the cells that help decompose the bone while the damaged part heals. In contrast, osteoblasts are the cells that facilitate bone mineralization and osteoid production. Osteoid is an organic substance present in the bone that further mineralizes to form a bone. Lastly, osteocytes come from the osteoblasts; they help form bone. Osteocytes also help in maintaining the right amount of calcium in the bone.
Fat Cells
Fat cells are also known as adipocytes. Adipocytes contain fats that can be used for generating energy. When the fat is stored, it becomes round and swollen. And when the body uses the fat, the cell gets shrinks to their original size. Adipose cells have also known to contain a special hormone that influences the sex hormone, blood pressure, and metabolism. Other than that, it also influences blood clotting along with cell signaling.

Nerve Cells
Neurons or nerve cells are the basic part of the nervous system. Our nerves send signals to the spinal cord, brain, and other body organs via nerve impulses. A neuron structure consists of nerve processes and the cell body.
The central body of the cell consists of cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles. Nerves extend from the cell body to transmit signals throughout the body.
Skin Cells
Our skin consists of epithelial layers supported by connective tissues and an underlying subcutaneous layer. The outer part of the skin is made of epithelial cells packed closely together.
The skin cells have a range of roles. It protects the internal part of the body from dehydration, damage, and germs, stores fat, and produces hormones and vitamins.

Endothelial Cells
Endothelial cells contribute to the inner lining of the lymphatic system and cardiovascular system structure. It forms the layer of blood vessels, organs, and lymphatic vessels, including skin, heart, lungs, and brain.
These types of cells also help in creating new blood vessels and angiogenesis. Endothelial cells also help regulate the movement of gases, macromolecules, and fluid between tissues and blood to manage blood pressure.
Sex Cells
Sex cells are also gametes, reproductive cells in both female and male gonads to make babies. Sperm or male sex cells have tail-like long projections known as flagella, whereas ova or female sex cells are non-motile and larger than male gametes.
For reproduction, sex cells unite in fertilization to give birth to a new cell/human. In the process, other body cells work in replicating mitosis via gametes.
Pancreatic Cells
our pancreas functions as an endocrine and exocrine organ which means the discharge of hormones directly into organs or through ducts. Pancreatic cells help to regulate concentration levels of blood glucose which helps to digest carbs, proteins, and fats.

Cancer Cells
unlike any other types of cells in the body, cancer cells work to demolish the body. Cancer results from abnormal cell properties causing teh cell to divide uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
Cancel cells originate from mutation stemming from radiation, chemicals, and UV light exposure. These cells also have genetic origins like cancer-causing virus DNA. Cancer cells spread rapidly because of decreased sensitivity to proliferate and anti-growth signals in the absence of stop commands. Programmed cell death and lack of Apoptosis make them more formidable.
Read More – Does Regular Exercise Prevent The Risk Of Cancer?
Conclusion:
Cells are tiny structures present in the human body. Every cell present in our body has different responsibilities and functions. They may have different roles in our bodies, but they rely on each other to function properly. The human body consists of 11 types of cells, each essential.